Difference between revisions of "Orographic Effects"
| Line 38: | Line 38: | ||
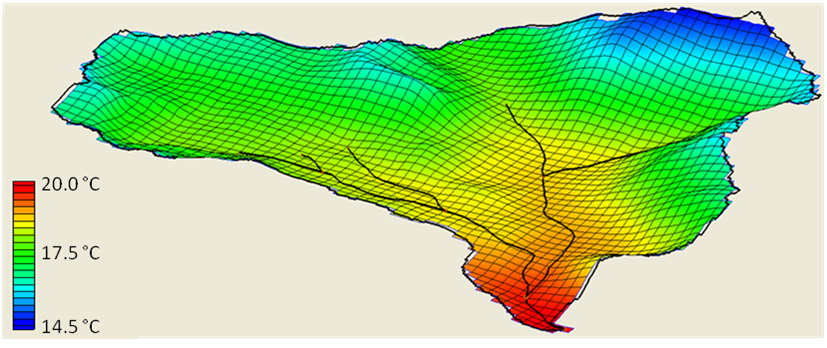
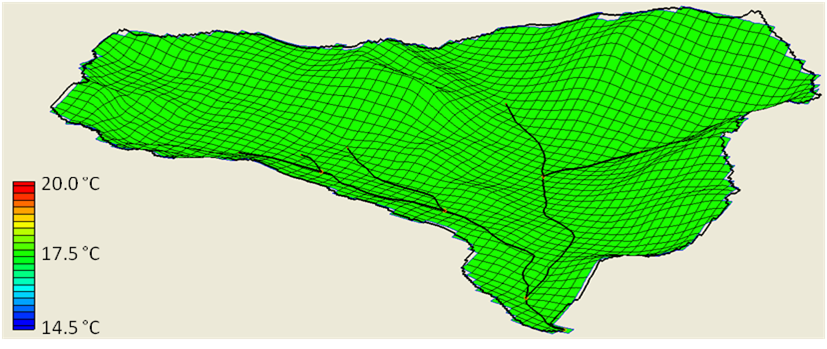
'''Basin with and without orographic effects'''<br> | '''Basin with and without orographic effects'''<br> | ||
| + | [[File:Orog2.png]] <br> | ||
[[File:Orog1.png]] <br> | [[File:Orog1.png]] <br> | ||
| − | |||
Revision as of 18:42, 28 November 2012
An orographic effect is the natural cooling of air masses as they rise from lower elevations to higher elevations due to terrain. GSSHA currently has two options for accounting for orographic effects. The user is able to define a constant lapse rate when only one temperature gage is located within the basin, and an option where GSSHA calculates the lapse rate hourly based on multiple temperature gage locations within the basin. For multiple temperature gages the file format required is shown below. Currently, only 1 additional temperature gage (in addition to the standard input hmet file) is allowed. The basic premise of the adjusted temperatures in each cell is shown in the equation below. The figures below demonstrates a uniform temperature profile for an entire basin, and a temperature profile that accounts for orographic effects.
|
|
Tadj = T - (Elevcell - Elevgage) * LR |
| Tadj = adjusted temperature (°C) |
| Ta = temperature measured at the gage site (°C) |
| Elevcell = elevation of grid cell (km) |
| Elevgage = elevation of gage site (km) |
| LR = lapse rate (°C km-1) |
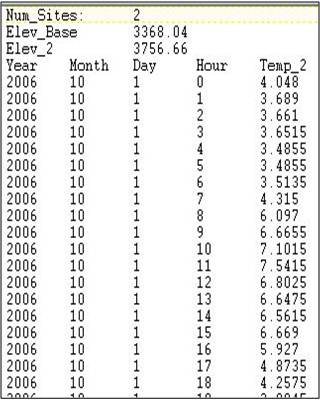
File Format for Multiple Temperature Gage Locations
Elevations are in meters, temperatures in Celsius.
Elev_Base is the elevation (m) of the gage site used for the main hmet file.
Elev_2 is the elevation (m) of the secondary gage site.